What are the 5 stages of steel material life cycle?
The steel material life cycle refers to the stages through which a product or material passes, from the extraction of raw materials to its eventual disposal. There are five stages of the material life cycle, each with its own set of challenges and environmental impacts. In this article, we will explore each stage of the material life cycle and examine the ways in which they contribute to environmental degradation.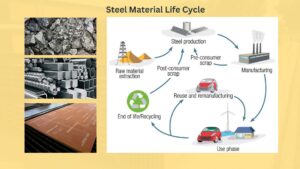
- Raw Material Extraction.
- Manufacturing & Processing.
- Transportation.
- Usage & Retail.
- Waste Disposal.
- Extraction The first stage of the material life cycle is the extraction of raw materials from the earth. This can include mining for metals, drilling for oil, or harvesting trees for lumber. The extraction process can be highly damaging to the environment, as it often involves the removal of large amounts of soil, rock, or vegetation. This can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution.
- Production After the raw materials are extracted, they are transported to a manufacturing facility where they are transformed into finished products. The production stage can be highly energy-intensive, as it requires large amounts of electricity, fuel, and water. The production of certain materials, such as plastics and chemicals, can also release toxic pollutants into the air and water.
- Distribution Once the products are manufactured, they need to be transported to their final destination. This can involve shipping, trucking, or air transport, all of which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and other forms of pollution. In addition, the packaging materials used to protect and transport products can also contribute to environmental degradation.
- Use The use stage is when the product is actually used by the consumer. This can involve anything from driving a car to using a cell phone to consuming food. During this stage, products can release pollutants into the air, water, or soil, or contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, the disposal of products after they are used can also lead to environmental problems.
- Disposal The final stage of the material life cycle is disposal. This can involve landfilling, incineration, or recycling. Landfilling and incineration can lead to the release of toxic pollutants into the air, water, and soil, while recycling can be energy-intensive and require large amounts of water. Even products that are recycled can eventually end up in a landfill, as not all materials can be recycled.
In conclusion, the material life cycle is a complex process that involves a variety of environmental impacts. Each stage of the life cycle can contribute to environmental degradation, from the extraction of raw materials to the disposal of finished products. By understanding the material life cycle and the ways in which it impacts the environment, we can begin to take steps to minimize our impact and reduce our consumption of resources.
Comments are closed.